SS 316/304L Seamless Tubing Manufacturing: Cold Rolling & Drawing Quality Control
Inconsistent tubing quality leads to costly equipment failures. This risk compromises entire industrial systems, threatening safety and productivity. Mastering cold rolling[^1] and drawing quality control is the only reliable solution.
Mastering quality control for SS 316/304L seamless tubing involves rigorous material preparation, precise cold rolling and drawing processes, and comprehensive inspection. This ensures superior strength, corrosion resistance, and dimensional accuracy for demanding industrial applications, preventing equipment failure and ensuring long-term reliability.
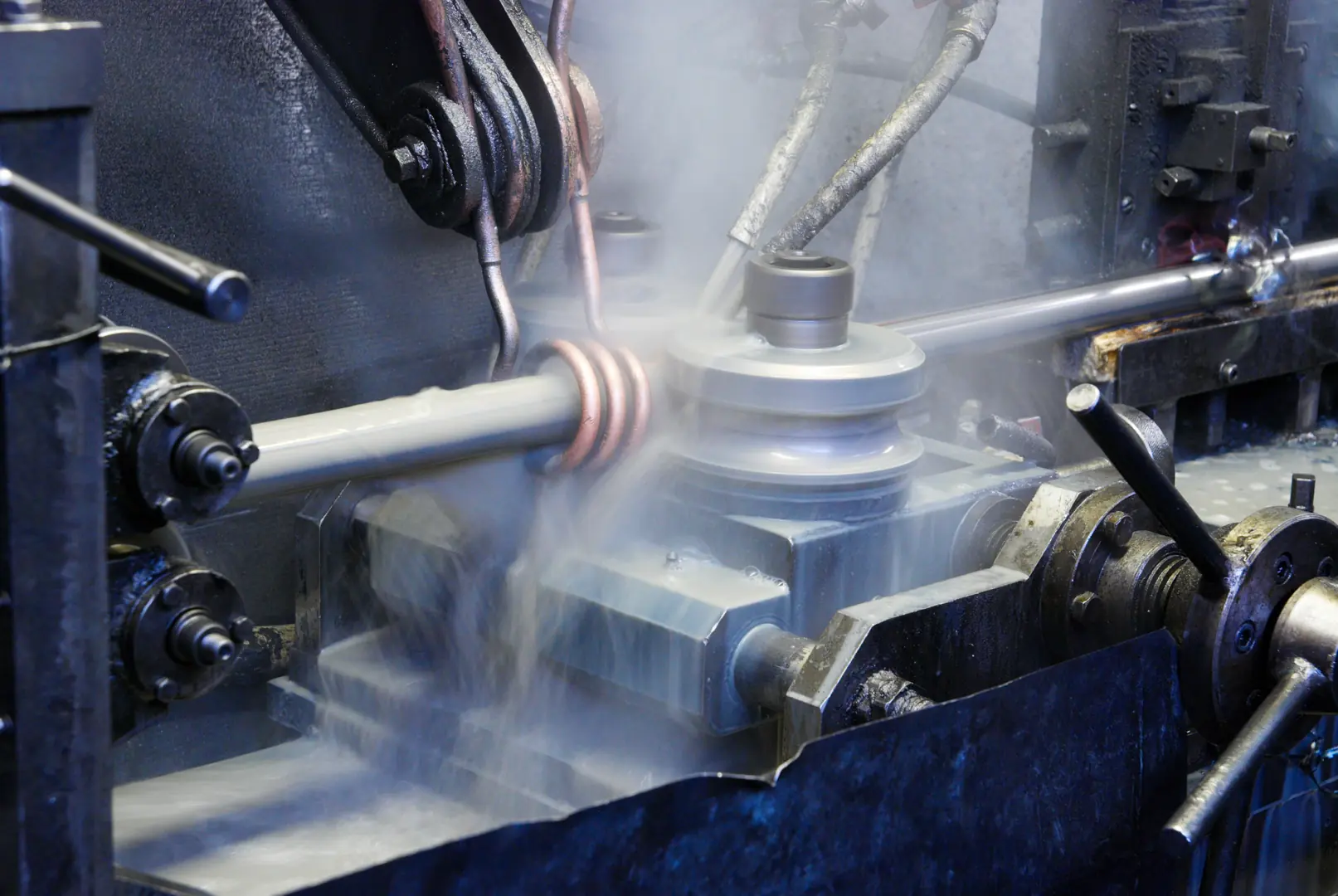

In my years as Global Business Director at MFY, I've seen firsthand that the difference between a standard product and a superior one lies in the details. For critical components like seamless tubing, "good enough" is never good enough. The integrity of a massive processing plant can depend on the quality of a single tube. That's why we don't just manufacture; we engineer confidence into every millimeter of our product. Let’s walk through the critical quality control stages that make this possible.
What are the initial steps in preparing SS 316/304L for seamless tubing?
Flawed raw materials lead to defective tubes. These hidden defects can cause catastrophic failures down the line. Our meticulous preparation process eliminates these risks right from the start.
Initial preparation involves selecting high-quality billets, followed by precise piercing to create a hollow shell. This is followed by thorough cleaning and annealing to ensure the material is uniform and ready for cold working, establishing the foundation for a flawless final product.

Everything starts with the raw material. You cannot build a strong house on a weak foundation, and you cannot make reliable tubing from subpar steel. I remember a case years ago where a new supplier tried to pass off billets with minor internal inconsistencies. Our initial inspection caught it, saving our client in the petrochemical industry from what could have been a disastrous system failure. This is why our process is non-negotiable.
Billet Inspection and Selection
Before any work begins, each solid bar, or "billet," undergoes a battery of tests. We conduct spectral analysis[^2] to verify the chemical composition is precisely within the 316 or 304L grade specifications. We also use ultrasonic testing[^3] to scan for any internal voids, cracks, or inclusions that are invisible to the naked eye. Only perfect billets proceed to the next stage.
| Inspection Parameter | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Spectral Analysis | Verifies correct alloy grade (e.g., Nickel, Chromium, Moly) |
| Internal Integrity | Ultrasonic Testing | Detects hidden cracks, voids, or impurities |
| Surface Quality | Visual & Magnetic Particle | Checks for external cracks, seams, or scale |
| Dimensions | Caliper Measurement | Ensures billet meets initial size specifications |
The Piercing and Annealing Cycle
Once a billet is approved, it's heated and pierced by a mandrel to create a "hollow." This is a high-stress process, so quality control is vital. After piercing, the hollow is annealed—heated and slowly cooled. This critical step relieves internal stresses, refines the grain structure, and prepares the steel for the intense pressures of cold rolling and drawing. It ensures the material is homogenous and ductile, preventing cracks during subsequent forming.
How does the cold rolling process enhance the quality of seamless tubing?
Standard tubing often lacks the precision for critical uses. Poor dimensional tolerances can mean leaks, improper fittings, and system failures. Cold rolling delivers the exact dimensions and superior finish required.
Cold rolling enhances quality by refining the grain structure, which significantly increases the tubing's strength and hardness. This process also achieves tight dimensional tolerances and a superior surface finish, making the final product ideal for high-pressure and sterile applications.
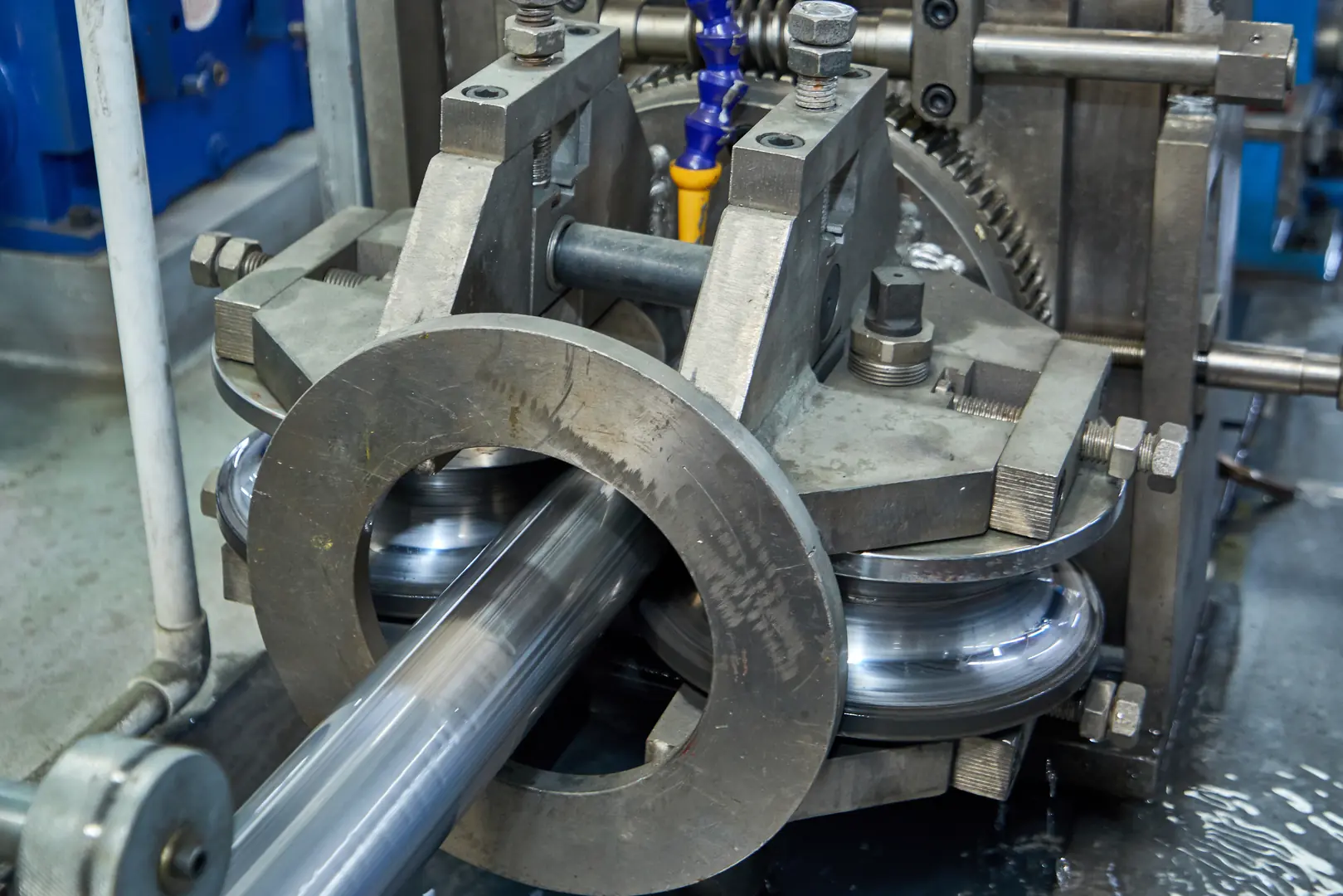

Cold rolling is where the tubing truly begins to take on its high-performance characteristics. It's a process of gradual reduction at room temperature, which fundamentally changes the steel's properties. Unlike hot rolling, which is primarily for shaping, cold rolling is for precision and strength. We are essentially compressing and refining the steel's microstructure, squeezing out imperfections and aligning the grains to create a much stronger, more resilient material. This is crucial for clients in sectors like pharmaceuticals or semiconductor manufacturing, where a perfectly smooth, non-corrosive internal surface is just as important as pressure tolerance.
Achieving Work Hardening and Grain Refinement
As the tube passes through the rollers, the steel's crystal structure is compressed and elongated. This phenomenon, known as work hardening[^4] or strain hardening, significantly increases its tensile strength and hardness. The grain structure becomes finer and more uniform, which not only improves mechanical properties but also enhances its resistance to certain types of corrosion. This is a key reason why cold-rolled seamless tubing is specified for harsh chemical environments.
Dimensional Precision and Surface Finish
The precision of the rollers and mandrels allows us to achieve incredibly tight tolerances on the tube's outer diameter, inner diameter, and wall thickness. This consistency is vital for automated welding, compression fittings, and any application where a perfect seal is required. Furthermore, the process imparts a smooth, clean surface finish, reducing the risk of bacterial growth in sanitary applications and improving fluid dynamics in hydraulic systems.
| Property | Before Cold Rolling (Annealed Hollow) | After Cold Rolling |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ~515 MPa | ~620 MPa or higher |
| Hardness | ~80 HRB | ~95 HRB or higher |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | High | Low (e.g., <0.8 µm) |
| Dimensional Tolerance | Loose | Tight (e.g., ±0.05mm) |
What are the key quality control measures during the drawing process?
The drawing process can introduce stress and defects. These invisible flaws can compromise the tube's integrity over time. We implement strict in-process controls to ensure perfection at every stage.
Key quality control measures during drawing include monitoring die and plug conditions, controlling lubrication for a smooth surface, and maintaining precise drawing speeds. We also conduct in-process dimensional checks and stress-relief annealing to ensure consistency and prevent material fatigue.
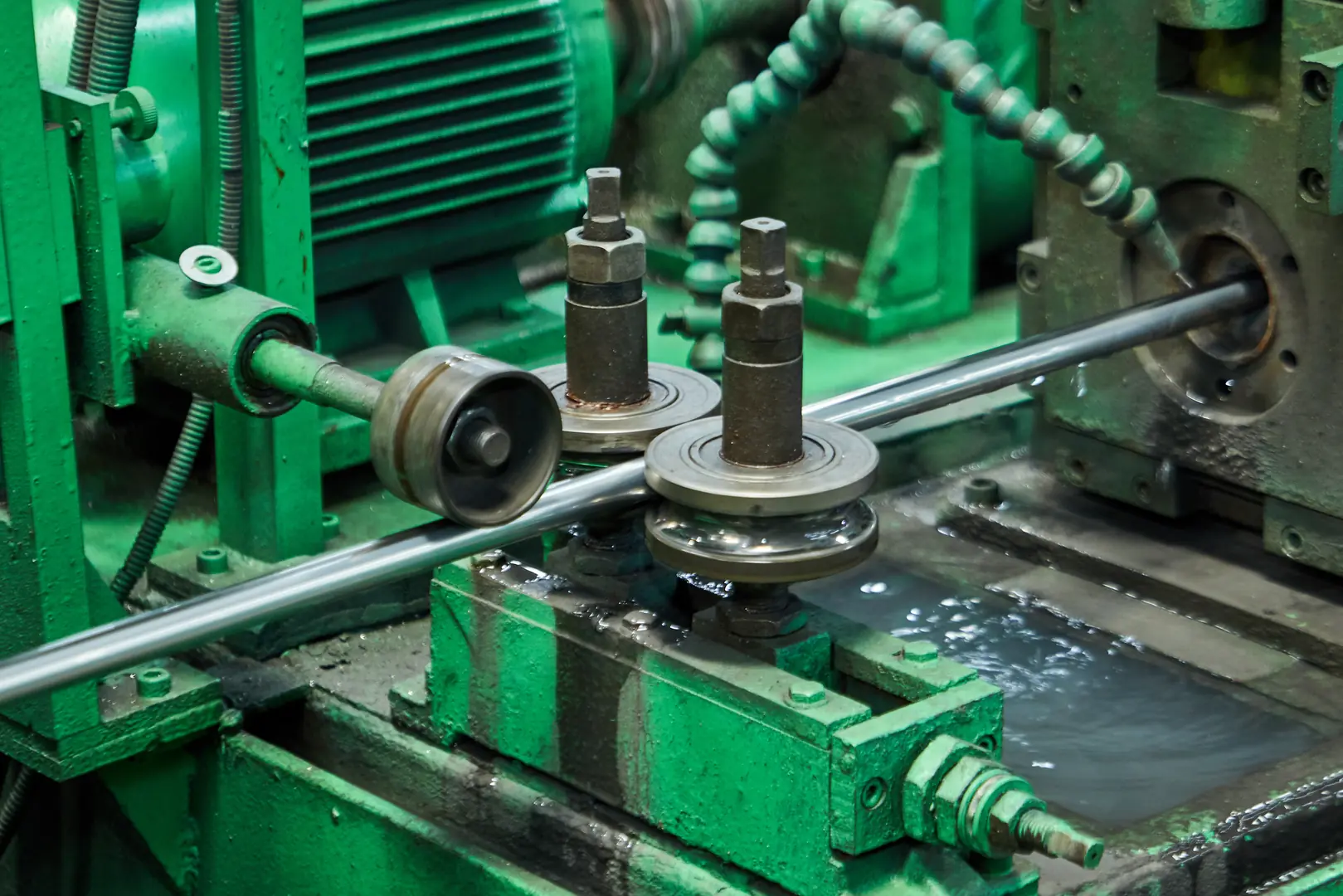

Cold drawing is the final step in achieving the exact dimensions and an even finer surface finish. The tube is pulled through a die that is smaller than its outer diameter, further reducing its size and refining its properties. This process requires finesse. I once visited a facility where they were having issues with surface scratching on their tubes. The problem was traced back to microscopic imperfections in their drawing die and inconsistent lubrication. It’s a perfect example of how small details have a huge impact. At MFY, we’ve moved beyond simple manual checks and are integrating technology to monitor these variables in real-time.
The Role of Lubrication and Tooling
The condition of the die and the internal plug (mandrel) is paramount. We use hardened, polished tooling and inspect it constantly for wear. Proper lubrication is just as critical; it creates a barrier between the tube and the die, preventing galling and ensuring a smooth, defect-free surface. The type and application of lubricant are carefully controlled based on the material and desired finish.
Advanced In-Process Monitoring
This is where our commitment to innovation comes into play. We are implementing automated sensor systems that monitor drawing force, temperature, and speed in real-time. An unexpected spike in drawing force can indicate a lubrication failure or a tooling issue, allowing our system to flag the problem instantly. This allows us to make immediate adjustments, preventing an entire production run from being compromised. This real-time data feedback loop is the future of quality control, moving from reactive inspection to proactive process optimization. This is how we guarantee that every meter of tubing is as perfect as the first.
How is the final inspection of SS 316/304L seamless tubing conducted?
You can't just assume a tube is perfect after manufacturing. A single missed flaw can lead to disaster in the field. Our multi-stage final inspection guarantees every tube meets or exceeds specifications.
Final inspection is a comprehensive process involving visual checks, precise dimensional measurements using calipers and micrometers, and non-destructive testing (NDT) like eddy current or ultrasonic tests. We also perform mechanical tests (tensile, hardness) and corrosion tests to validate material properties.

After all the forming and heat treatment, the final inspection is our last line of defense. This is our promise to the customer. It's a systematic process designed to verify every aspect of the tube's quality, from its dimensions to its hidden microstructural integrity. We combine human expertise with advanced technology to ensure nothing is overlooked. An engineering contractor for an LNG project once told me that our detailed inspection reports give them the confidence to install our products in their most critical systems. That's the value we aim to deliver.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
NDT allows us to inspect the tube's integrity without damaging it. Every single tube passes through an NDT line.
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT): This is excellent for detecting surface and near-surface defects like cracks, pits, and seams.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): This method sends sound waves through the material to find deeper, internal flaws, such as inclusions or laminations, and to verify wall thickness with extreme accuracy.
Mechanical and Chemical Validation
We take samples from each production batch for destructive testing to confirm the material's properties meet the required standards. This data validates that our entire process is performing as expected.
| Test Type | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Visual & Dimensional | Human & Laser Inspection | Checks for surface perfection and confirms OD, ID, and wall thickness. |
| Non-Destructive (NDT) | Eddy Current / Ultrasonic | Detects hidden surface and internal flaws on 100% of tubes. |
| Mechanical | Tensile, Hardness, Flattening Tests | Confirms strength, ductility, and durability under stress. |
| Corrosion | Intergranular Corrosion Test | Verifies the material's resistance to corrosion, especially after welding. |
What are the best practices for maintaining quality in cold rolling and drawing?
Maintaining consistent quality is a constant challenge. A single slip-up can damage your equipment and your reputation. Adhering to proven best practices ensures unwavering excellence.
Best practices include rigorous operator training, scheduled maintenance of machinery and tooling, and maintaining a clean production environment. Implementing a robust Quality Management System (QMS) with full traceability from raw material to finished product is also absolutely essential for consistent results.
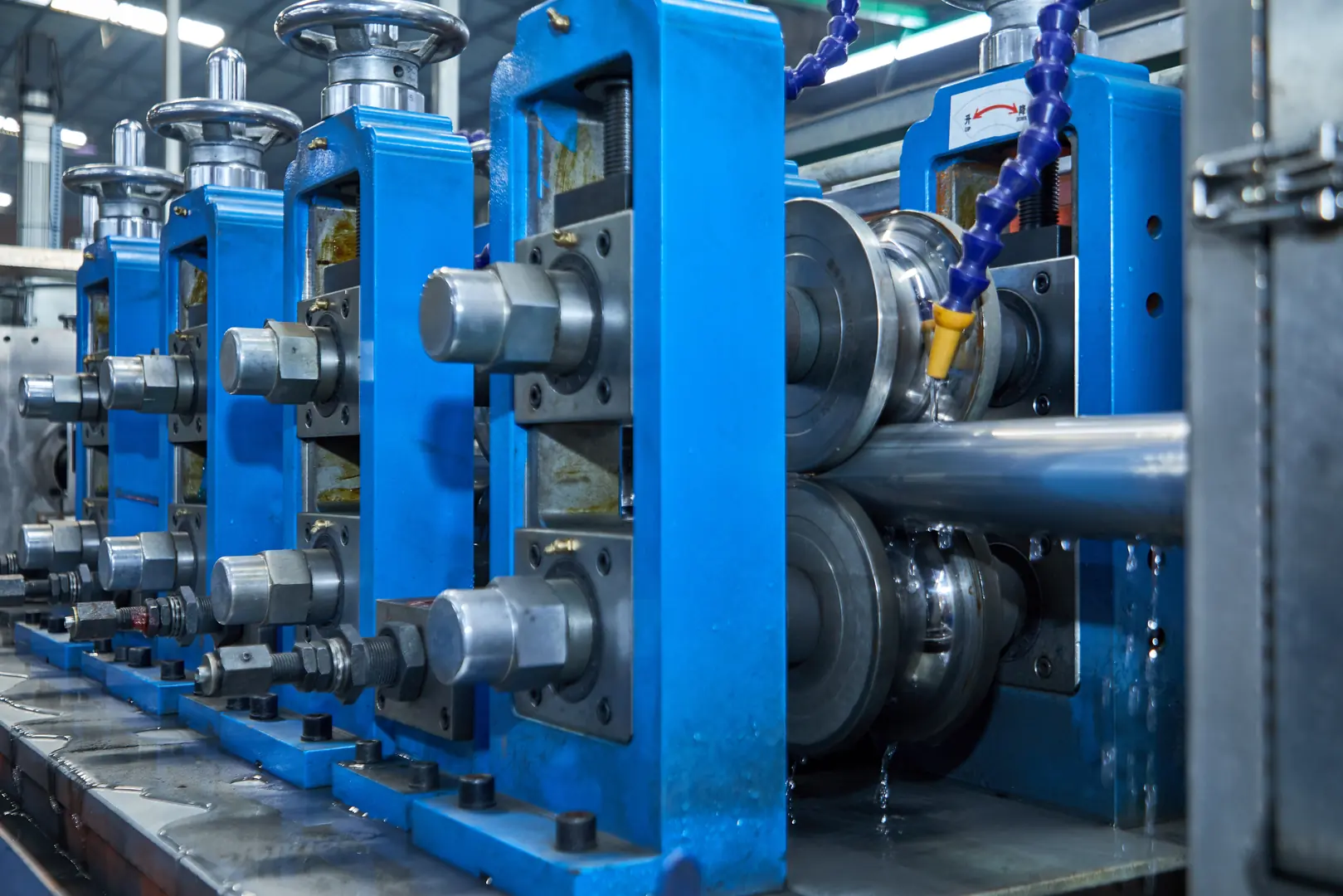
Excellent quality control isn't just about a final inspection; it's a culture embedded in the entire manufacturing process. It's about empowering people with the right training, giving them the best tools, and building systems that support consistency. You can have the most advanced machines in the world, but if your team isn't trained or your processes aren't documented, you will never achieve consistent, world-class quality. This holistic approach is what separates the leaders from the rest of the pack.
The Human Element: Training and Expertise
Our operators are our first line of quality control. They are extensively trained to understand the nuances of the machinery, to spot subtle changes in the process, and to feel a sense of ownership over the product. Regular training on new techniques and quality standards is mandatory. An experienced operator can often hear or see a problem long before a sensor can detect it.
The Future: Smart Manufacturing and IoT
Looking ahead, we are heavily investing in IoT and smart manufacturing. By embedding sensors throughout our production line, we can collect data on every variable—from machine temperature to vibration to lubrication viscosity. This data feeds into a central system that uses AI to identify trends and predict potential issues before they occur. This creates a fully traceable, transparent production history for every tube we make. For our customers, this means an unprecedented level of quality assurance and a supply chain partner who is ready for the future of industry.
Conclusion
In SS 316/304L seamless tubing, quality isn't an accident. It's the result of precise control at every step, from billet to final inspection. This meticulous process is how we deliver the reliability and performance your critical applications demand, ensuring your long-term success.
Have Questions or Need More Information?
Get in touch with us for personalized assistance and expert advice.







