Precision Tubing: Small Diameter SS Selection Guide for Instruments & Automation
Selecting the wrong precision tubing causes system failure. This uncertainty risks project delays and costly rework. We provide a clear selection guide for guaranteed performance and reliability.
Selecting the right small diameter stainless steel tubing involves identifying application requirements, evaluating material properties like corrosion resistance, assessing environmental compatibility, considering manufacturing precision, and choosing a reliable supplier. This ensures operational accuracy, safety, and long-term system efficiency in instrumentation and automation.

As the Global Business Director at MFY, I've seen countless projects where the success of a multi-million dollar automation system hinged on something as small as a few meters of tubing. The choice is far more than a simple material specification; it's a foundational decision that impacts everything from measurement accuracy to operational safety and long-term maintenance costs. Getting it right from the start is not just an advantage, it's a necessity. Let's walk through the critical steps to ensure you make the right investment for your high-performance systems.
What Are the Key Requirements for Instrumentation and Automation Tubing?
Vague specifications lead to mismatched tubing. This causes leaks, pressure drops, and inaccurate measurements. Define these key requirements first to ensure perfect system integration and performance.
Key requirements include precise dimensional tolerances (OD, ID, wall thickness), high pressure ratings, specific temperature ranges, corrosion resistance to the process fluid, and an excellent internal surface finish to ensure clean, uninterrupted flow for sensitive instruments.
In the world of precision instruments and automation, "close enough" is never good enough. The tubing is often the artery of the system, responsible for transporting critical fluids for control, analysis, or actuation. Any deviation can have cascading effects. I remember a client in the semiconductor industry who was experiencing inconsistent results from their gas chromatography equipment. After weeks of troubleshooting complex electronics, we discovered the issue was improperly specified tubing with a rough internal surface that was trapping trace amounts of previous samples. This highlights why a detailed analysis of requirements is the non-negotiable first step. It's an investment in operational accuracy and lifecycle efficiency.
Core System Specifications
Before you even think about material grades, you must have a clear picture of the physical and operational demands. This goes beyond simple dimensions and requires a holistic view of the system's function.
| Requirement | Critical Consideration | Impact on System |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | Maximum operating and surge pressures. | Prevents ruptures, leaks, and ensures safety. |
| Temperature Range | Both ambient and process fluid temperatures. | Affects material strength and resistance to creep. |
| Dimensional Tolerance | OD, ID, and wall thickness consistency. | Ensures leak-proof connections with fittings. |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | Internal surface roughness. | Critical for purity, flow dynamics, and preventing contamination. |
Application-Specific Needs
Beyond the core specs, consider the unique demands of your application. Are you dealing with high-purity gases for medical devices? Or aggressive chemicals in a processing plant? Each scenario demands a different level of scrutiny. For fluid control systems, the internal diameter's consistency is paramount for predictable flow rates. For high-pressure hydraulic lines in automated machinery, wall thickness and material strength are the top priorities. Documenting these needs creates a clear blueprint for your ideal tubing.
Which Stainless Steel Grades Are Best for Small Diameter Tubing?
Choosing the wrong steel grade invites corrosion. This compromises system integrity and safety. Select from proven grades like 304L or 316L for a reliable, long-lasting solution.
The best stainless steel grades for small diameter tubing are typically austenitic types like 316/316L for superior corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides, and 304/304L for general-purpose applications. Both offer excellent formability and weldability for complex instrumentation systems.

The material grade is the heart of your tubing's performance. While there are many stainless steel alloys, the 300 series, specifically 304L and 316L, dominate the instrumentation field for good reason. These austenitic grades provide a fantastic balance of corrosion resistance, strength, and workability. Recent advancements in metallurgy have led to cleaner, more consistent alloys, enhancing the microstructural integrity and dimensional stability of the final product. At MFY, we've invested heavily in sourcing raw materials that meet these stringent modern standards, because we know that the quality of the final tube begins with the quality of the initial melt.
The Workhorse: Grade 304/304L
Think of 304L as the versatile and reliable standard for a huge range of applications. It offers excellent corrosion resistance in most environments and is more cost-effective than its 316L counterpart. It's perfect for pneumatic control lines, hydraulic systems, and instrumentation where the fluid is not overly corrosive and there's no exposure to saltwater or harsh chlorides. The "L" designation indicates low carbon content, which improves weldability by minimizing carbide precipitation.
The Premium Choice: Grade 316/316L
When the stakes are higher, 316L is the grade of choice. The addition of molybdenum is the key differentiator, providing significantly enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly from chlorides. This makes it essential for marine environments, chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food-grade applications. While it comes at a higher price point, the investment pays for itself in longevity and safety where 304L would fail.
| Feature | Grade 304/304L | Grade 316/316L |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good general resistance. | Excellent, especially against chlorides. |
| Primary Alloy Additions | Chromium, Nickel | Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum |
| Common Applications | Pneumatics, hydraulics, general instrumentation. | Chemical processing, marine, pharma, food & bev. |
| Relative Cost | Lower | Higher |
How Do Environmental and Operating Conditions Affect Tubing Selection?
Ignoring the operating environment leads to premature failure. This results in unexpected downtime and maintenance costs. Assess these factors to ensure your tubing withstands real-world conditions.
Environmental conditions like humidity, salinity (marine environments), and exposure to chemicals dictate the required corrosion resistance. Operating conditions such as high pressure, extreme temperatures, and mechanical vibration influence the necessary material strength, wall thickness, and fatigue resistance of the tubing.

A common mistake I see is engineers focusing solely on the internal process fluid while forgetting about the external environment where the tubing will live. I once worked with a client on a coastal LNG facility. They had correctly specified tubing for the cryogenic internal temperatures, but used a grade susceptible to chloride corrosion. Within a few years, the salty sea air had caused significant external pitting, compromising the entire system's integrity. This costly lesson underscores the need for a 360-degree assessment of all conditions, both inside and out. The tubing must be robust enough to handle the entire operational envelope, not just one part of it.
External Environmental Threats
The world outside the tube is often just as aggressive as the fluid inside. You must consider factors like humidity, which can accelerate general corrosion; salinity, which demands the chloride resistance of 316L; and exposure to industrial chemicals or cleaning agents. If the tubing is part of a larger machine, you also have to account for potential leaks of other fluids, like hydraulic oils or coolants, that could come into contact with its surface.
Internal Operating Demands
Inside the tube, the challenges are different. High-pressure applications require thicker walls and potentially seamless manufacturing for maximum integrity. Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can affect the steel's mechanical properties, so the grade must be rated for that range. One of the most overlooked factors is mechanical vibration. In automation equipment with motors and pumps, constant vibration can lead to fatigue failure at connection points. In these cases, selecting tubing with good ductility and ensuring proper clamping and support is just as important as choosing the right material grade.
What Manufacturing and Customization Options Matter for Precision Tubing?
Standard off-the-shelf tubing may not fit your design. This forces compromises and complex workarounds. Customization ensures your tubing meets exact specifications for seamless integration and optimal performance.
Key manufacturing options include seamless versus welded tubing, with seamless offering higher pressure integrity. Important customizations involve precise cut-to-length services, specific surface finishes (e.g., electropolishing), tight dimensional tolerances, and custom bending or coiling to fit complex automation layouts.
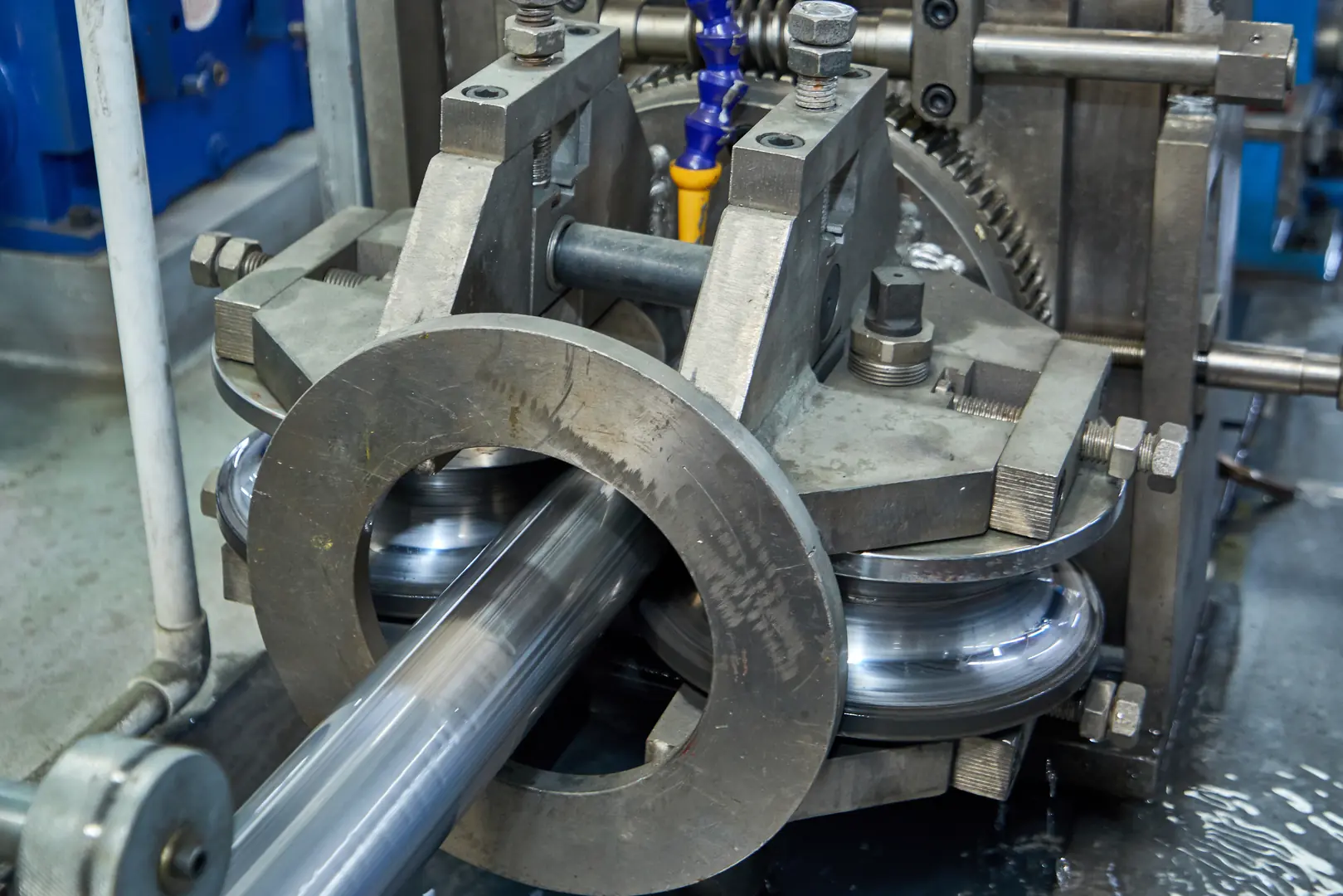

The difference between a good system and a great one often comes down to the manufacturing details. How the tube is made and finished has a direct impact on its performance and reliability. As automation and instrumentation become more compact and complex, the ability to get tubing that is precisely tailored to the application is a massive competitive advantage. It reduces installation time, eliminates potential points of failure from extra fittings, and optimizes system flow dynamics. This is where partnering with a manufacturer who has advanced capabilities becomes a strategic decision, not just a procurement one.
Seamless vs. Welded: The Core Decision
This is one of the first manufacturing choices you'll face. Welded tubing is made from a strip of steel that is rolled and welded along the seam. It's generally more cost-effective and available in longer continuous lengths. Modern welding techniques are excellent, but the seam remains a potential weak point. Seamless tubing is extruded from a solid billet, resulting in a homogenous structure with no weld seam. This gives it superior pressure ratings and corrosion resistance, making it the standard for critical high-pressure applications.
| Feature | Welded Tubing | Seamless Tubing |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | Good | Excellent |
| Uniformity | Good wall consistency. | Can have slight wall variations. |
| Cost | More economical. | Higher cost. |
| Best Use Case | General instrumentation, structural. | High-pressure, critical systems. |
Value-Added Customization
Beyond the basic manufacturing method, look for a supplier who can provide services that simplify your assembly process. Precise, burr-free cutting to length is fundamental. For high-purity applications, options like electropolishing can create an ultra-smooth internal surface that resists particle adhesion. Custom bending and coiling can deliver a component that fits perfectly into your equipment, saving you valuable time and labor.
How Can You Choose a Reliable Supplier for Precision Tubing?
A poor supplier delivers inconsistent quality. This disrupts your production and damages your reputation. Partner with a supplier who guarantees quality, consistency, and supply chain stability.
Choose a reliable supplier by verifying their quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), reviewing material test reports (MTRs), assessing their manufacturing capabilities and inventory levels, and confirming their ability to provide consistent quality and on-time delivery for supply chain stability.

After all the technical analysis, your decision ultimately rests on the partner you choose. A supplier is more than just a vendor; they are an extension of your own quality control and supply chain. In today's volatile global market, a supplier's stability, transparency, and commitment to quality are paramount. As automation accelerates, the demand for tubing that meets stringent, evolving industry standards will only grow. Aligning with a forward-thinking supplier future-proofs your systems against technological shifts and regulatory demands.
Beyond the Price Tag: Quality Assurance
Never make a decision on price alone. Always demand a Material Test Report (MTR)[^1] or 3.1 certificate for every batch of tubing. This document is your proof of the material's chemical composition and mechanical properties, providing full traceability back to the source. Check for ISO 9001 certification[^2], which demonstrates a commitment to a robust quality management system. A good supplier will be proud to share this documentation and will have a rigorous internal inspection process for things like dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and defect detection.
The Strategic Partnership
The ideal supplier acts as a partner. They should have the technical expertise to discuss your application and help you refine your specifications. At MFY, our integrated supply chain—from raw materials to finished product—gives us an unparalleled level of control over quality and delivery schedules. We believe in agility and resilience, which means maintaining strong inventory levels and having the production capacity to respond quickly to our clients' needs. A truly reliable partner offers not just a product, but also peace of mind, knowing that your critical components will arrive on time and to the exact standard you require, every single time.
Conclusion
Selecting the right small diameter SS tubing is an investment in precision and reliability. By focusing on requirements, materials, conditions, and a strong supplier partnership, you future-proof your instrumentation and automation systems for peak performance and a long lifecycle.
Have Questions or Need More Information?
Get in touch with us for personalized assistance and expert advice.







